Interagency Agreement
Challenge
The Treasury Department had mandated that all federal agencies begin using G-Invoicing, their shared services platform which helps agencies manage intragovernmental (IGT) buy and sell transactions for interagency agreements. Our client, as a mid-to-large federal agency, did business with numerous federal trading partners and managed hundreds of interagency agreements annually. Furthermore there were over 20-plus business and program offices and over a dozen or more applications at the agency impacted, including their enterprise resource planning (ERP) platform, which was itself managed by a third party partner. Moreover there were many process challenges with the way these business lines managed agreements; there was no one single standard process being used:
- Program offices developed & managed agreements on behalf of trading partners, essentially hand-holding them through-out the process
- Excessive back & forth communications to sheppard the approval process across multiple internal & external offices and agencies
- Attachments were used to circumvent forms where forms were seen complicated or data not applicable, in many cases
- Unnecessary redo of multi-year agreements every year because it was easier to sync with the fiscal year funding cycle
- Lack of a common platform to collaborate and communicate
- No centralized tracking or authoritative source of agreements and orders
- No standard workflow for agreements management
Our client quickly realized that given the magnitude of the implementation, they needed to have an enterprise-level understanding of the current state of all business processes and capabilities as well as applications and data integrations that were affected. More specifically, they knew that there were no standard processes used to develop interagency agreements So they wanted to have an enterprise view of all workflow processes that took into account those business offices who developed interagency agreements manually versus those that used ordering portals. Their expectations were that with this enterprise level understanding, they could begin to develop a standardized process for agreement development and be better positioned to comply with the mandate.
Solution
The OmniSolve enterprise architecture team worked with the client and key stakeholders to discuss possible approaches. This was going to be a multi-year program given the number of business lines and applications affected. The client was keen on making an early impression and wanted to focus on what was achievable right away. To that end, they opted to focus on those business lines who developed agreements manually, meaning they did not use any ordering portals. OmniSolve developed a 5-point plan and roadmap which included following areas of focus:
- Research & data collection
- Current state business process analysis and architectures
- Future state business process analysis and architectures
- Gap analysis and standard workflow recommendations
- Implementation guidance and change management
Outcome
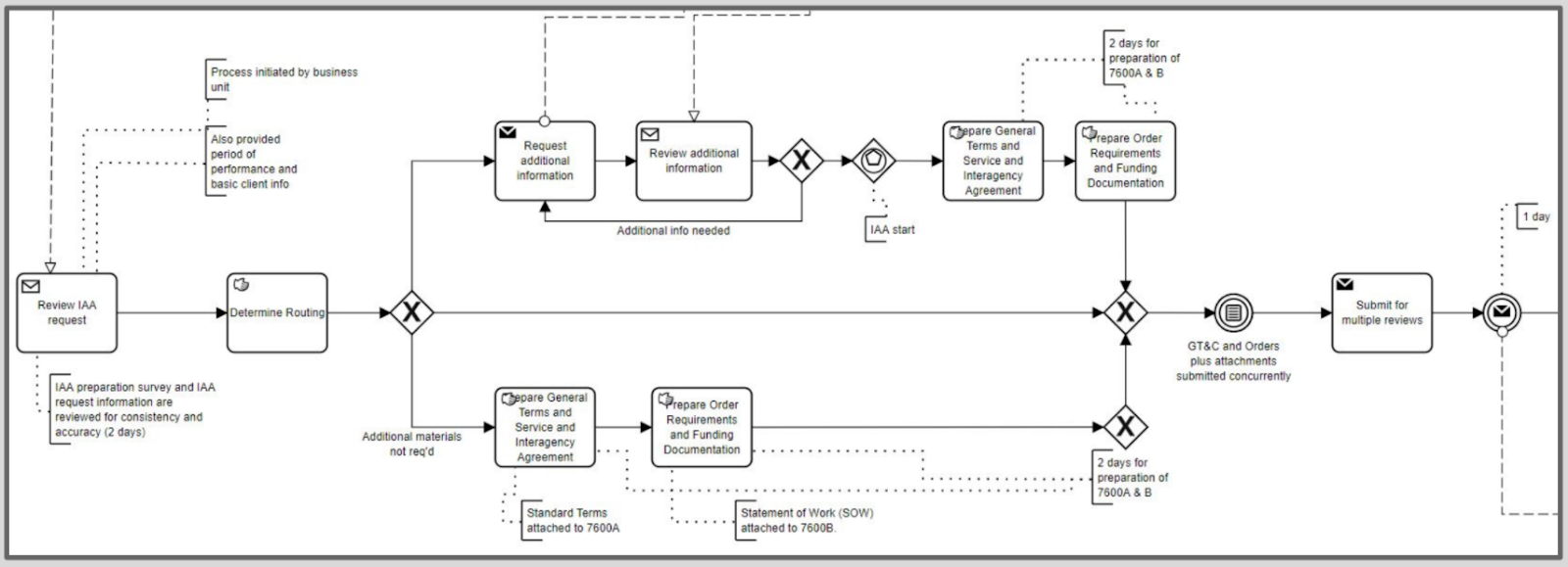
With the plan in place OmniSolve’s enterprise architecture team began their analysis and data collection. The team developed business process models using Trisotech based upon interviews with business lines of their current agreement processes. Using these models, the enterprise architecture team observed pain points and determined gaps in the current workflow. The team then developed standardized business process models which addressed these gaps and developed recommendations on what these business lines should consider when implementing G-Invoicing.
The team published the Gap Analysis and Standard Workflow recommendations document. This document outlined the following recommendations which the client would base their change management plans:
- Data centralization and governance considerations
- Centralized & transparent view of end to end agreements data pipeline
- Predictive / forecast reporting & analytics on billing settlements and cash flow at an agency and business line level
- Broader finance oversight given billing readiness is dependent on agreements and order data integrity and governance
- Automation of repetitive process steps for a more standardized workflow (examples such as trading partner readiness communications, data validations and billing reconciliations, document version control and signature approvals)
- Automation of low value work using robotic process automation technologies to interpret and take action on routine tasks while directing action on exceptions
Technologies & Methodologies
 |
 |
| Trisotech | Visio |
Featured Experts